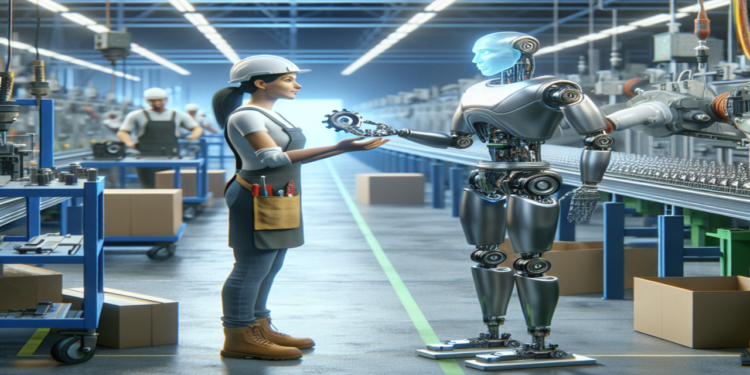
The landscape of manufacturing has undergone a remarkable transformation, shifting from traditional manual labor to advanced robotic automation. As industries face increasing pressures to enhance efficiency and productivity, assembly robots have emerged as pivotal players in modern factories. This article explores how these innovative machines are redefining the manufacturing process, the technologies driving this change, and the implications for the workforce.
Defining Assembly Robots: Types and Capabilities
Assembly robots come in various forms, each designed to meet specific production needs. The most common types include:
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): These are designed to work alongside human operators, enhancing productivity without replacing the human touch. Cobots are user-friendly and can be easily programmed for different tasks, making them ideal for smaller manufacturers.
- Industrial Robots: Typically larger and more powerful, these robots are often used for high-speed, repetitive tasks. They excel in environments that require high precision and are commonly seen in automotive and electronics manufacturing.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): These robots navigate factory floors independently, transporting materials and components between workstations. They play a crucial role in optimizing logistics within manufacturing facilities.
Key technologies driving the capabilities of an assembly robot include advanced sensors, machine vision systems, and artificial intelligence. These technologies allow robots to perform complex tasks with high precision and adaptability, ensuring they can be deployed across diverse applications.
The Strategic Advantages of Robotic Assembly
The transition to robotic assembly offers numerous strategic advantages for manufacturers:
Boosting Productivity
Assembly robots can operate continuously, significantly increasing production rates. Unlike human workers, they do not require breaks, can work around the clock, and can be programmed to complete tasks more rapidly. This enhanced speed translates to higher throughput, enabling manufacturers to meet growing market demands efficiently.
Quality Assurance
One of the most significant benefits of using assembly robots is their ability to maintain consistent quality. Robots are programmed to perform tasks with high precision, minimizing human error and variability. Advanced machine vision systems can detect defects in real time, ensuring that only products meeting quality standards move forward in the assembly process.
Cost-Efficiency
While the initial investment in robotic systems can be substantial, the long-term savings often outweigh these costs. Robotic assembly reduces labor costs and minimizes material waste due to improved precision. Additionally, the increased efficiency and productivity can lead to a quicker return on investment (ROI), making it a financially sound decision for many manufacturers.
Innovations Fueling the Robotics Revolution
The advancements in robotics technology are driving a new wave of automation in manufacturing:
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the capabilities of assembly robots. By employing machine learning algorithms, robots can adapt to new tasks and improve their performance over time. This adaptability is crucial for manufacturers looking to remain competitive in a rapidly changing market.
Integration with IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a significant role in modern manufacturing. By connecting robots to a network of sensors and devices, manufacturers can monitor performance in real time, gather data on production efficiency, and make informed decisions to optimize processes. This level of connectivity enables proactive maintenance and reduces downtime.
Advanced Robotics Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as soft robotics, are expanding the applications of assembly robots. Soft robots can handle delicate materials and products, making them ideal for industries like food and consumer goods. These innovations enhance the versatility of robotic systems, allowing for a broader range of tasks.
Workforce Dynamics in the Age of Automation
The rise of robotic assembly brings changes to workforce dynamics:
The Shift in Workforce Roles
As assembly robots take on repetitive tasks, the roles of human workers are evolving. Instead of performing mundane, manual tasks, workers are increasingly focusing on oversight, programming, and maintenance of robotic systems. This shift allows employees to engage in more complex and fulfilling work.
Training and Reskilling Initiatives
To adapt to these changes, companies must invest in training and reskilling their workforce. Providing employees with the skills needed to work alongside robots is essential for maximizing the benefits of automation. This includes understanding how to program and troubleshoot robotic systems, as well as the ability to analyze data generated by IoT devices.
Enhancing Human-Robot Collaboration
The most effective manufacturing environments will be those where humans and robots work in harmony. Collaborative robots are designed to facilitate this partnership, allowing for a seamless integration of human intuition and robotic precision. Establishing a culture of collaboration will be vital for successful automation strategies.
The Impact of Robotics on Supply Chain Efficiency
The integration of assembly robots significantly enhances supply chain efficiency. By automating key processes, manufacturers can reduce lead times and optimize inventory management. Robots streamline workflows, ensuring that components are assembled quickly and accurately, minimizing bottlenecks. This not only accelerates production but also allows for better alignment with market demands, enabling manufacturers to respond rapidly to changes in consumer preferences and maintain a competitive edge in a fast-paced environment.
Conclusion
The shift from manual to robotic assembly is reshaping the landscape of manufacturing, offering significant advantages in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. As assembly robots continue to evolve, they will play an essential role in driving the future of factories. Embracing this technological revolution will enable manufacturers to thrive in an increasingly competitive environment, paving the way for a new era of collaboration between humans and machines.